Indepth information about RTMP Server
Online video technology, known as Real-Time Messenger Protocol, or RTMP for short, has greatly influenced the growth of streaming internet video.
Professional broadcasters and streaming service providers widely use it to give live and on-demand programs to millions of viewers worldwide.
We’ll discuss the technical details of RTMP, describe how it functions, and go through some common RTMP streaming use cases in this post.
How Does RTMP Work?
A TCP-based protocol, RTMP, keeps connections for low-latency audio and video streaming open. Streams are divided into smaller units known as packets to enhance the amount of data that can be delivered smoothly. RTMP specifies the number of virtual channels that operate independently for the delivery of packets. This implies that audio and video are concurrently supplied on different channels.
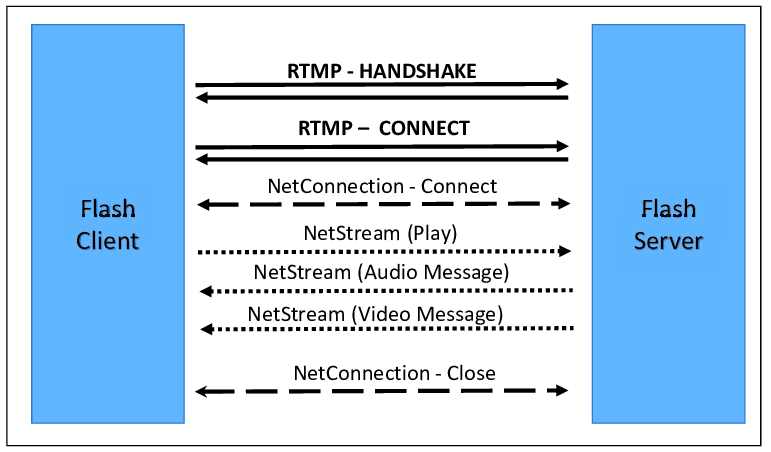
The 3-step process
At a high level, Real-Time Messaging Protocol works as a three-step process.
Step 1: The handshake
After RTMP creates a TCP connection, it performs a handshake by having the client and server exchange three packets. These bundles are known as chunks.
The procedure seems as follows:
-
The client transmits a chunk to inform the server of the protocol version it is utilizing.
-
The client transmits another chunk with a timestamp before waiting for a response.
-
The server replies with an echo of the chunks it had received, along with a timestamp for when it did.
-
The server replies to the client’s final packet, a copy of the timestamp packet.
-
The handshake is deemed complete once the last packet exchange is finished.
STEP 2: The Connection
During the connection phase, the client and server exchange coded messages. The connection’s secret language is called Action Message Format (AMF). His conversation seeks to establish rapport so that streaming may start.
In essence, the client and server employ a message sequence during this phase to negotiate a connection.

STEP 3: The Stream
Once the capture is complete, and the connection has been established successfully, the stream should be available. Despite the complexity of this process, technology is designed to facilitate speedy travel.
How To Set Up RTMP?
The Real-Time Messaging Protocol must be set up with an encoder (hardware or software), a sensing device that provides feedback. As well as being necessary an RTMP server or online video platform (OVP) is needed to broadcast the stream to your audience.
1. Connect your gear or software for RTMP encoding to your video source (camera).
2. Start a new live stream on your RTMP or OVP server.
3. Set the OVP’s encoding parameters.
4. Enter the RTMP URL to enable RTMP delivery.
5. Fill out the RTMP configuration settings on your encoder using your stream name and RTMP URL.
6. View the stream in real time.
7. Start streaming
While we offer the information on setting up an RTMP Server, we would like you to test our own:
TRY FOR FREE FOR 5 DAYS! RTMP TRIAL
What are the benefits of the RTMP protocol?
Because of its low latency, flexibility, and simplicity in integrating various media, RTMP is a widely used protocol.
In conclusion, the main advantages of RTMP are:
-
Low latency
-
Flexible
-
Easy to integrate different media
Low Latency
Stable video connections are ensured via low latency. Fast streams with no lag are advantageous for viewers of live-streaming content like webinars.
Flexible
Due to the flexibility of the RTMP protocol, viewers can consume feeds in any order they like. RTMP feeds allow for skipping, rewinding, and joining after they have started instead of being required to be watched linearly.
Easy To Integrate
The RTMP protocol enables users to merge many media types into a single source. This proves that combining text, audio, and video is possible. There may also be more media channel alternatives. For instance, MP3 and AAC audio streams can be transmitted via RTMP.
The RTMP server will distribute the screen-sharing stream to endpoints as required once it has been configured. Viewers using a compatible media player or web browser can view the screen-sharing session in real-time.
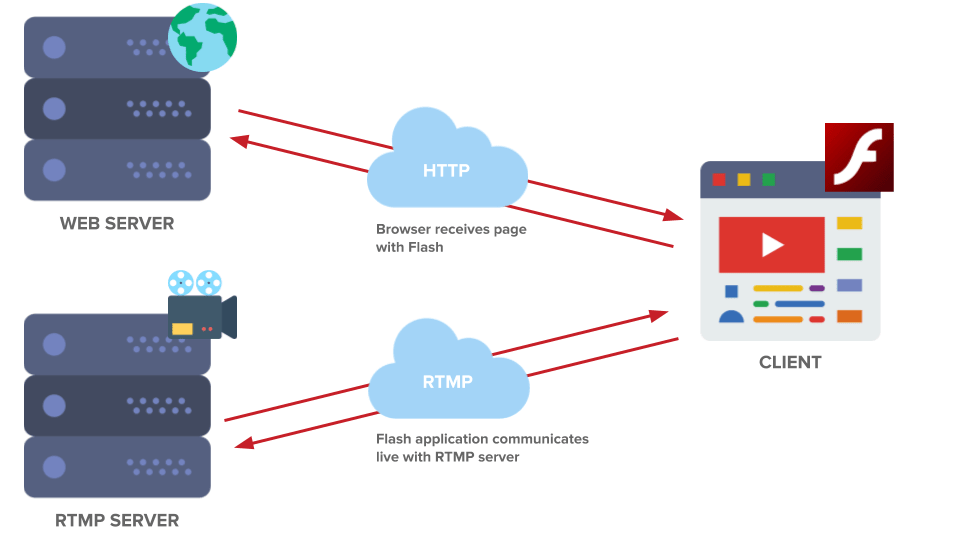
RTMP vs. HTTP Streaming
While HTTP-based protocols rely on standard web servers to maximize the viewing experience and expand efficiently, streaming protocols like Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) carry video utilizing dedicated streaming servers.
RTMP and HTTP streaming differs in several significant ways, including:
Advantages of RTMP
-
Supported AAC, AAC-LC, HE-AAC+, v1, v2, MP3 audio codecs
-
Supported H.264, VP6, VP8, Screen Video v1 & v2 video codecs
-
A Minimum of Buffering
-
Less latency (5 seconds)
-
A variety of formats, including RTMPS, RTMPE, RTMPT, and RTMFP
RTMP Disadvantages
-
Not extensively supported
-
No longer being maintained.
Benefits of the HTTP Protocol
-
Supports streaming at an adaptive bitrate
-
Quick and simple to set up
-
No need for additional plugins or software
-
Better live streaming support with decreased latency
-
Protection of content
-
Trustworthy
-
Ability to scale
-
Reduced latency
HTTP Disadvantages
-
Frequently needs transmuxing
-
Since it is an Apple proprietary technology, it has yet to be widely supported.
Conclusion
RTMP and HTTP are two of the most frequently used protocols today. Every one of them has advantages and disadvantages. RTMP, a TCP-based protocol, is widely used because it permits persistent connections and low-latency streaming. On the other hand, HTTP streams live and on-demand content at varying bitrates using an HTTP-based protocol. It frequently performs better than RTMP since it has less latency.
So which one should you choose? Everything depends on what you require. If you need low latency, RTMP is a better option. However, HTTP is a better option if you need changeable bitrate streaming.


Recent Comments